55 Degrees C To F
marihuanalabs
Sep 24, 2025 · 5 min read
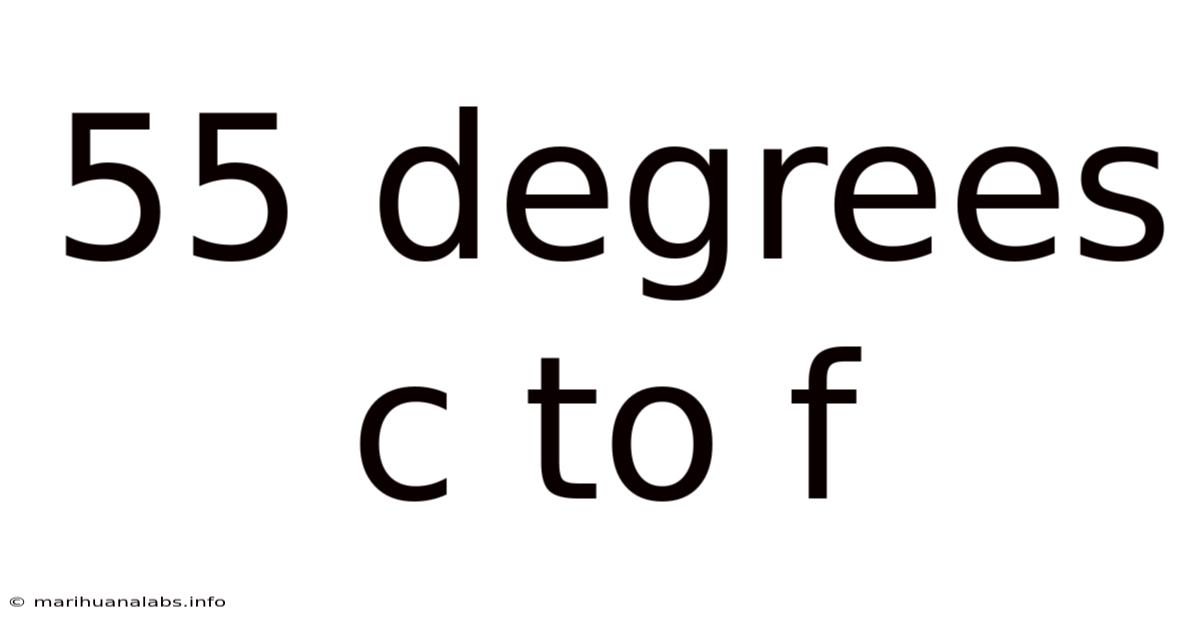
Table of Contents
Converting 55 Degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit: A Comprehensive Guide
Are you struggling to convert 55 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit? Understanding temperature conversions is crucial in many fields, from cooking and baking to meteorology and engineering. This comprehensive guide will not only show you how to convert 55°C to °F but also delve into the underlying principles of temperature scales, provide practical examples, and answer frequently asked questions. We'll explore the history of these scales, their limitations, and why understanding this conversion is so important.
Understanding Celsius and Fahrenheit
Before jumping into the conversion, let's understand the two scales involved. Celsius (°C), also known as the centigrade scale, is a metric unit of temperature. It's based on the freezing and boiling points of water, set at 0°C and 100°C respectively, at standard atmospheric pressure. Fahrenheit (°F) is another temperature scale, predominantly used in the United States. Its freezing and boiling points of water are 32°F and 212°F, respectively, again at standard atmospheric pressure.
The key difference lies in the scale's increments. The Celsius scale has 100 degrees between the freezing and boiling points of water, while the Fahrenheit scale has 180 degrees. This difference is the root of the conversion calculations.
The Conversion Formula: From Celsius to Fahrenheit
The formula for converting Celsius (°C) to Fahrenheit (°F) is:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Let's apply this formula to convert 55°C to °F:
°F = (55 × 9/5) + 32
°F = (11 × 9) + 32
°F = 99 + 32
°F = 131
Therefore, 55 degrees Celsius is equal to 131 degrees Fahrenheit.
Practical Applications and Examples
Understanding temperature conversions is vital in various situations:
-
Cooking and Baking: Many recipes, especially those originating from different countries, use different temperature scales. Accurately converting temperatures ensures the perfect outcome of your culinary creations. Imagine trying to bake a cake with an oven temperature off by 20 degrees – the result might be disastrous!
-
Medicine and Healthcare: Body temperature is frequently measured in both Celsius and Fahrenheit. Converting between the two is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment. A slight difference in temperature readings can alter medical decisions.
-
Meteorology and Climate Science: Weather reports often present temperatures in both Celsius and Fahrenheit. Understanding the conversion helps in interpreting weather information accurately, regardless of the reporting scale used.
-
Engineering and Manufacturing: Many industrial processes require precise temperature control. Converting between Celsius and Fahrenheit is crucial to ensure equipment operates within the specified parameters. Inaccurate conversions can lead to malfunctions or even safety hazards.
-
Travel and International Communication: Traveling to different countries means encountering varying temperature scales. Knowing how to convert temperatures enables you to dress appropriately and stay comfortable.
A Deeper Dive into Temperature Scales: History and Development
The Celsius and Fahrenheit scales have interesting histories. Anders Celsius, a Swedish astronomer, developed the Celsius scale in 1742, initially with 0° representing the boiling point and 100° representing the freezing point of water. This was later reversed to the scale we use today.
Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, a German physicist, developed the Fahrenheit scale in 1724. His scale was based on three reference points: the freezing point of a brine solution (0°F), the freezing point of water (32°F), and human body temperature (approximately 96°F). Fahrenheit's original scale differed slightly from the modern Fahrenheit scale, with some adjustments made later.
Limitations of Celsius and Fahrenheit
While both scales are widely used, they have limitations:
-
Arbitrary Zero Points: Both scales use arbitrary zero points, meaning the zero point doesn't represent the absolute absence of heat. This makes comparisons of temperature differences less straightforward than using an absolute temperature scale.
-
Different Increment Sizes: The differing increment sizes (100 vs 180 degrees between water's freezing and boiling points) make conversions necessary and can sometimes lead to confusion.
-
Negative Temperatures: The possibility of negative temperatures on both scales can be problematic in some calculations and interpretations.
Absolute Temperature Scales: Kelvin and Rankine
To address the limitations of Celsius and Fahrenheit, absolute temperature scales were developed. Kelvin (K) is the absolute temperature scale in the metric system, with 0 K representing absolute zero – the theoretical point at which all molecular motion ceases. Rankine (°R) is the absolute temperature scale corresponding to Fahrenheit. Both Kelvin and Rankine scales eliminate negative temperatures.
Converting Celsius to Kelvin and Fahrenheit to Rankine
The conversions between Celsius and Kelvin, and Fahrenheit and Rankine, are relatively straightforward:
- Kelvin (K) = °C + 273.15
- Rankine (°R) = °F + 459.67
Alternative Conversion Methods
Beyond the standard formula, there are other ways to convert 55°C to °F:
-
Online Converters: Numerous websites and apps provide instant temperature conversions. These are convenient but might not enhance your understanding of the underlying principles.
-
Temperature Conversion Charts: Charts showing corresponding Celsius and Fahrenheit values can be helpful for quick reference, but may not be as precise as using the formula.
-
Mental Estimation: With practice, you can develop a sense for approximate conversions. For instance, you can remember that a 10°C increase roughly corresponds to an 18°F increase.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: Why are there different temperature scales?
A: Different scales arose historically due to independent development and differing needs across various scientific and practical applications.
- Q: Which scale is more accurate?
A: Both Celsius and Fahrenheit are accurate within their defined ranges. However, the Kelvin scale offers a more fundamental and precise representation of temperature due to its absolute zero point.
- Q: Are there other temperature scales besides Celsius, Fahrenheit, Kelvin, and Rankine?
A: Yes, other historical scales exist, but these four are the most commonly used today.
- Q: What if I need to convert a temperature range instead of a single point?
A: Apply the conversion formula to both the lower and upper limits of the temperature range.
- Q: Can I use a calculator to perform the conversion?
A: Yes, any standard calculator can perform the necessary calculations.
Conclusion
Converting 55 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit, resulting in 131 degrees Fahrenheit, is a straightforward process using the formula °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32. However, this article goes beyond a simple conversion, providing a comprehensive understanding of temperature scales, their historical context, and their applications in various fields. Mastering temperature conversions is a valuable skill, applicable in everyday life, professional settings, and scientific pursuits. Remember the importance of accurate conversion, particularly in applications where precision is paramount, such as cooking, medicine, and engineering. By understanding the principles behind the conversions, you can confidently navigate the world of temperature measurement.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Borges And Me Film 2024
Sep 24, 2025
-
How To Draw Regular Pentagon
Sep 24, 2025
-
When Is The 16th Century
Sep 24, 2025
-
A Good Walk Spoiled Quote
Sep 24, 2025
-
Definition Of Specialisation In Economics
Sep 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 55 Degrees C To F . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.