38c Is What In Fahrenheit
marihuanalabs
Sep 21, 2025 · 5 min read
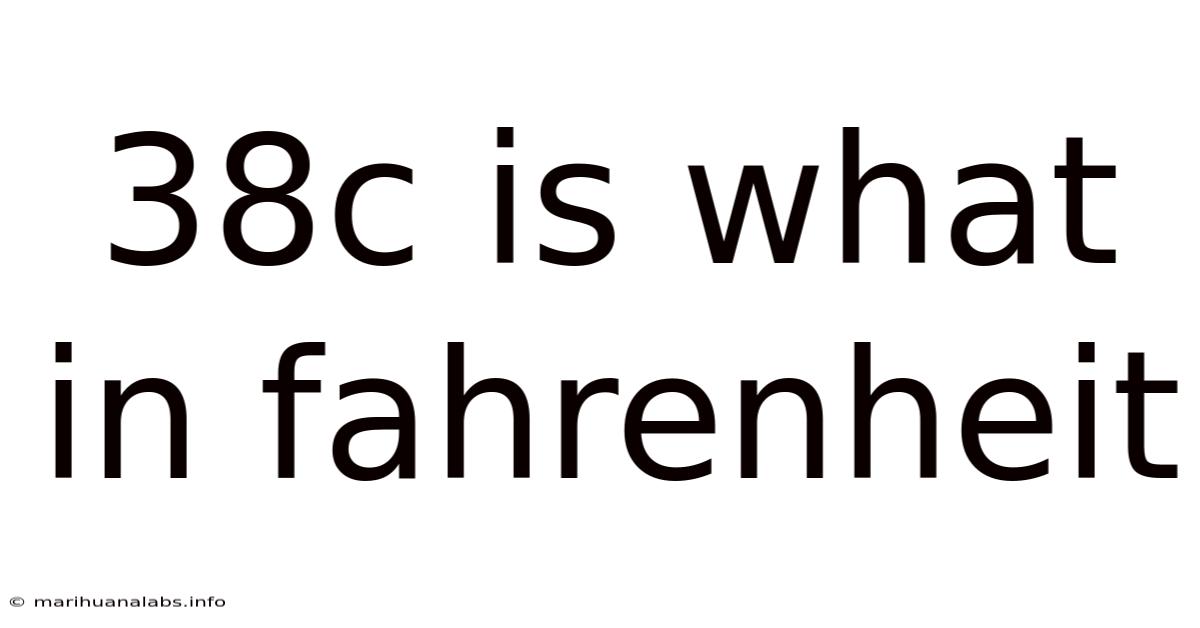
Table of Contents
38°C is What in Fahrenheit? Understanding Temperature Conversions
Ever wondered what 38°C translates to in Fahrenheit? This seemingly simple question opens the door to a fascinating exploration of temperature scales, their history, and the practical applications of converting between them. Understanding temperature conversion isn't just about plugging numbers into a formula; it's about grasping the fundamental differences between Celsius and Fahrenheit and appreciating their respective roles in our daily lives and scientific endeavors. This article will delve deep into the conversion process, explain the underlying science, and answer frequently asked questions about temperature scales.
Understanding Celsius and Fahrenheit
Before we jump into the conversion, let's establish a clear understanding of the two scales. Both Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F) are used to measure temperature, but they differ significantly in their reference points.
-
Celsius: The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is based on the freezing and boiling points of water. Zero degrees Celsius (0°C) represents the freezing point of water, and 100°C represents its boiling point, both at standard atmospheric pressure. This scale is widely used globally, particularly in scientific contexts and most of the world's countries.
-
Fahrenheit: The Fahrenheit scale, while less common internationally, remains prevalent in the United States. Its reference points are less intuitive. Zero degrees Fahrenheit (0°F) was originally defined as the freezing point of a specific brine solution (water, ice, and ammonium chloride), while 96°F was originally set as the average human body temperature. The freezing and boiling points of water at standard atmospheric pressure are 32°F and 212°F respectively.
Converting 38°C to Fahrenheit: The Formula and Process
The conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a straightforward mathematical process. The formula is:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Let's apply this formula to convert 38°C to Fahrenheit:
°F = (38°C × 9/5) + 32
°F = (7.2 × 9) + 32
°F = 64.8 + 32
°F = 96.8
Therefore, 38°C is equal to 96.8°F.
Beyond the Calculation: A Deeper Look at the Formula
The formula itself reveals the fundamental difference in the scale’s increments. The factor 9/5 (or 1.8) reflects the fact that a 1°C change corresponds to a 1.8°F change. Adding 32 accounts for the difference in the freezing point of water between the two scales (0°C vs. 32°F). This seemingly simple addition is crucial to accurately represent the temperature.
Practical Applications and Significance of Temperature Conversion
Understanding temperature conversion is vital in numerous contexts:
-
International Communication: With global interconnectedness, accurate temperature conversion ensures clear communication across regions using different temperature scales. Misunderstanding temperatures can have serious consequences, especially in fields like meteorology, aviation, and medicine.
-
Scientific Research: Scientific experiments often require precise temperature control and reporting. Converting between Celsius and Fahrenheit is essential for ensuring consistency and comparability of results across different studies and laboratories worldwide.
-
Engineering and Manufacturing: Many engineering processes, especially those involving materials science and thermal processes, require precise temperature control. Converting between scales is crucial for maintaining accurate measurements and ensuring the quality of manufactured goods.
-
Healthcare: Body temperature is often measured and recorded in both Celsius and Fahrenheit. Understanding the conversion is critical for healthcare professionals to quickly and accurately assess a patient's condition. Similarly, understanding the temperature settings of medical equipment is essential for optimal functionality and patient safety.
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes can be written in either Celsius or Fahrenheit. Accurate conversion is necessary to achieve the desired results and prevent culinary disasters. The difference of even a few degrees can impact the outcome significantly.
The History of Temperature Scales: A Brief Overview
The development of temperature scales is a fascinating chapter in the history of science. While the scales we use today are refined versions, their origins are rooted in earlier attempts to quantify temperature.
-
Early attempts: Early attempts to measure temperature were often rudimentary and lacked standardization. Different substances and reference points were used, leading to inconsistencies in measurement.
-
Fahrenheit scale (1724): Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit developed his mercury-in-glass thermometer and proposed his scale. While the reference points have evolved slightly since his initial proposal, the Fahrenheit scale remains in use today.
-
Celsius scale (1742): Anders Celsius, a Swedish astronomer, introduced a scale where 0° represented the boiling point of water and 100° its freezing point. This was later inverted to the modern Celsius scale we use today.
-
Kelvin scale (1848): Lord Kelvin, a British physicist, proposed an absolute temperature scale, the Kelvin scale, where 0 Kelvin (0 K) represents absolute zero, the theoretical point where all molecular motion ceases. The Kelvin scale is primarily used in scientific contexts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Q: Why are there two different temperature scales? A: Different scales arose independently due to historical reasons and the different perspectives of scientists involved in their development. The use of both scales continues due to their continued prevalence in different regions and specific applications.
-
Q: Which scale is more accurate? A: Both scales are equally accurate in measuring temperature. The difference lies in their reference points and the magnitude of the degrees.
-
Q: Is there an easier way to convert temperatures besides using the formula? A: While the formula is reliable, online converters and even some calculators offer quick and convenient temperature conversion tools. However, understanding the underlying formula remains essential for comprehending the relationship between the two scales.
-
Q: What is a normal body temperature in both Celsius and Fahrenheit? A: A normal human body temperature is approximately 37°C or 98.6°F. It's important to note that this can vary slightly depending on individual factors and measurement methods.
Conclusion: Mastering Temperature Conversion
Understanding the conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit is more than just a simple mathematical exercise. It's a key to unlocking a deeper understanding of temperature measurement, its historical development, and its diverse applications in science, technology, and everyday life. By grasping the underlying principles and the significance of the conversion formula, we can appreciate the nuances of these different temperature scales and their vital roles in our world. The conversion of 38°C to 96.8°F is just one example within a larger context of understanding and utilizing temperature measurements effectively. Remember, accuracy in temperature conversion is not merely a matter of calculation but a crucial element in communication, scientific rigor, and many other areas of life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
20 30 As A Percentage
Sep 21, 2025
-
Does Melania Trump Speak Russian
Sep 21, 2025
-
Gcse Jekyll And Hyde Quotes
Sep 21, 2025
-
Feast Of Corpus Christi Procession
Sep 21, 2025
-
What Are Variances In Accounting
Sep 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 38c Is What In Fahrenheit . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.